As part of the AI and vocational education and training project funded through the EU Erasmus plus project we are producing a series of case studies of the use of AI in VET in five European countries. Here is my first case study – the Ada chatbot developed at Bolton College.
About Bolton College
Bolton College is one of the leading vocational education and training providers in the North West of England, specialising in delivering training – locally, regionally and nationally – to school leavers, adults and employers. The college employs over 550 staff members who teach over 14,500 full and part time students across a range of centres around Bolton. The college’s Learning Technology Team has a proven reputation for the use of learning analytics, machine learning and adaptive learning to support students as they progress with their studies.
The Ada Chatbot
The Learning Technology Team has developed a digital assistant called Ada which went live in April 2017. Ada, which uses the IBM Watson AI engine, can respond to a wide range of student inquiries across multiple domains. The college’s Learning Technology Lead, Aftab Hussain, says “It transforms the way students get information and insights that support them with their studies.” He explains: “It can be hard to find information on the campus. We have an information overload. We have lots of data but it is hard to manage. We don’t have the tools to manage it – this includes teachers, managers and students.” Ada was first developed to overcome the complexity of accessing information and data.
Student questions
Ada is able to respond to student questions including:
- General inquiries from students about the college (for example: semester dates, library opening hours, exam office locations, campus activities, deadline for applying for university and more);
- Specific questions from students about their studies (for example: What lessons do I have today/this afternoon/tomorrow? Who are my teachers? What’s my attendance like? When is my next exam? When and where is my work placement? What qualifications do I have? What courses am I enrolled in? etc.)
- Subject specific inquiries from students. Bolton College is teaching Ada to respond to questions relating to GCSE Maths, GCSE English and the employability curriculum.
Personalised and contextualised learning
Aftab Hussein explains: “We are connecting all campus data sets. Ada can reply to questions contextually. She recognises who you are and is personalised according to who you are and where you are in the student life cycle. The home page uses Natural Language Processing and the Watson AI engine. It can reply to 25000 questions around issues such as mental health or library opening times etc. It also includes subject specific enquiries including around English, Mathematics and business and employability. All teachers have been invited to submit the top 20 queries they receive. Machine learning can recognise the questions. The technical process is easy.” However, he acknowledges that inputting data into the system can be time consuming and they are looking at ways of automatically reading course documentation and presentations.
All the technical development has been undertaken in house. As well as being accessible through the web, Ada, has both IOS and Android apps and can also be queried though smart speakers.
The system also links to the college Moodle installation and can provide access to assignments, college information services and curriculum materials. The system is increasingly being used in online tutorials providing both questions for participants and access to learning materials for instance videos including for health and social care.
It is personalised for individuals and contextualised according to what they are doing or want to find out. Aftab says: “We are looking at the transactional distance – the system provides immediate feedback reducing the transactional distance. “
Digital assessment
Work is also being undertaken in developing the use of the bot for assessment. This is initially being used for the evaluation of work experience, where students need to provide short examples of how they are meeting objectives – for example in collaboration or problem solving. Answers can uploaded, evaluated by the AI and feedback returned instantly.
Nudging
Since March 2019, the Ada service has provided nudges to students with timely and contextualised information, advice and guidance (IAG) to support their studies. The service nudges students about forthcoming exams, their work placement feedback and more. In the following example, a student receives feedback regarding his work placement from his career coach and employer.
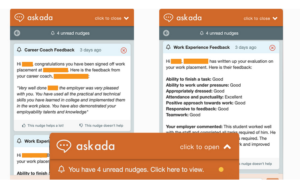
The College is currently implementing ProMonitor, a service which will offer teachers and tutors with a scalable solution for managing and supporting the progress made by their students. Once ProMonitor is in place, Ada will be in a position to nudge students about forthcoming assignments and the grades awarded for those assignments. She will also offer students advice and guidance about staying on track with their studies. Likewise, Ada will nudge teachers and student support teams to inform them about student progress; allowing for timely support to be put in place for students across the College.
A personal lifelong learning companion
For Aftab Hussein the persona of the digital agent is important. “In the future”, he says, “every child will have a personal lifelong learning companion which will support teaching and learning.” He thinks they will probably come from the big platform suppliers. Children will have their digital assistant from age the age of 3 or 4 and will have a Personal Learner Number allowing data to be exchanged between different institutions,
 The International Labour Organization (ILO) have launched a E-Discussion on Continuing online learning and skills development in times of the COVID-19 crisis. The discussion started on 27 March and runs to 9 April.
The International Labour Organization (ILO) have launched a E-Discussion on Continuing online learning and skills development in times of the COVID-19 crisis. The discussion started on 27 March and runs to 9 April.
