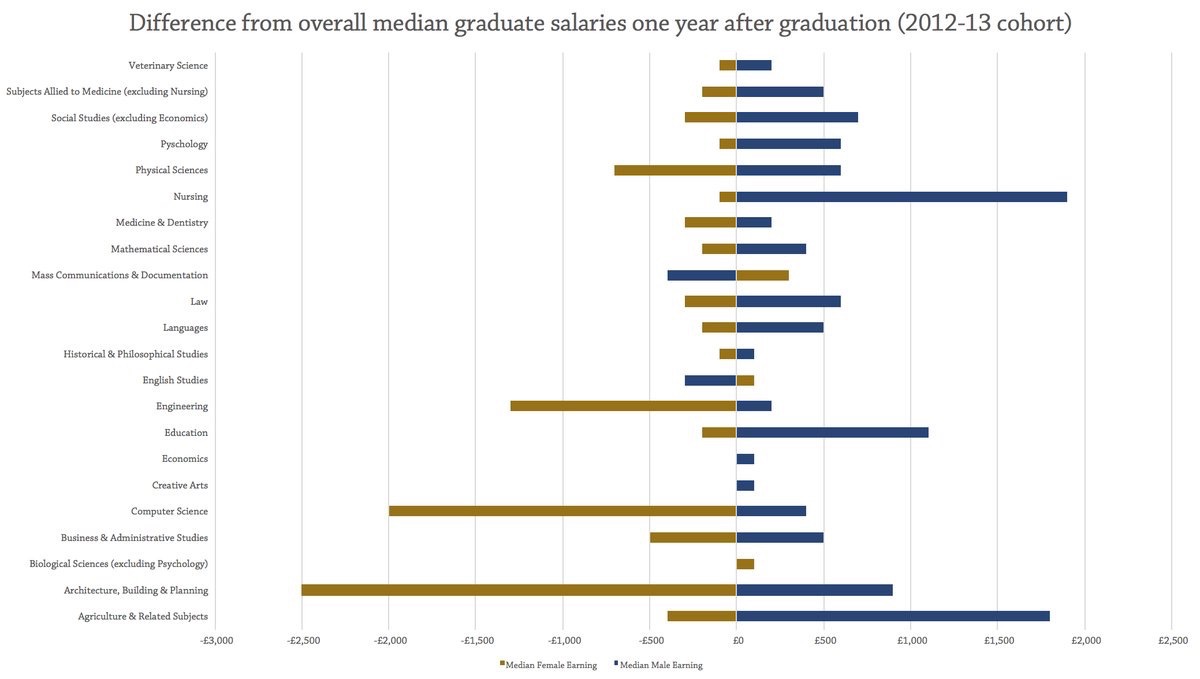
In our work on Labour Market Information Systems, we frequently talk about the differences between labour market information and labour market intelligence in terms of making sense and meanings from statistical data. The graph above is a case in point. It is one of the outcomes of a survey on Graduate Employment, undertaken by the UK Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA).
Like many such studies, the data is not complete. Yet, looking at the pay by gender reveals what WONKHE call “a shocking picture of the extent of the pay gap even straight out of university, and how different subject areas result in a diverse range of pay differences.”
Understanding why there is such a gap is harder. One reason could be that even with equal pay legislation, employers simply prefer to employ male staff for higher paid and more senior jobs. Also, the graph shows the subject in which the students graduated, not the occupational area in which they are employed. Thus the strikingly higher pay for mean who undertook nursing degrees may be due to them gaining highly paid jobs outside nursing. Another probable factor in explaining some of the pay gap is that the figures include both full and part time workers. Nationally far more women are employed part time, than men. However, that explanation itself raises new questions.
The data from HESA shows the value of data and at the same time the limitations of just statistical information. The job now is to find out why there is such a stark gender pay gap and what can be done about it. Such ‘intelligence’ will require qualitative research to go beyond the bald figures.